Sustainability is not a new concept; it has been in existence for decades but the concept became more popular after series of global catastrophes such as the use of chemical bombs in world wars, the Great Depression, collapse of corporations due to mismanagement as seen in the global financial crisis, inhumane working conditions as witnessed in the fashion industry, extinction of endangered species, destruction of forests due to upsurge in urbanization, etc. In present days, the emergence of COVID-19 has revealed to the world that current generations must act responsibly to ensure that the human race and the earth it inhabits are preserved.
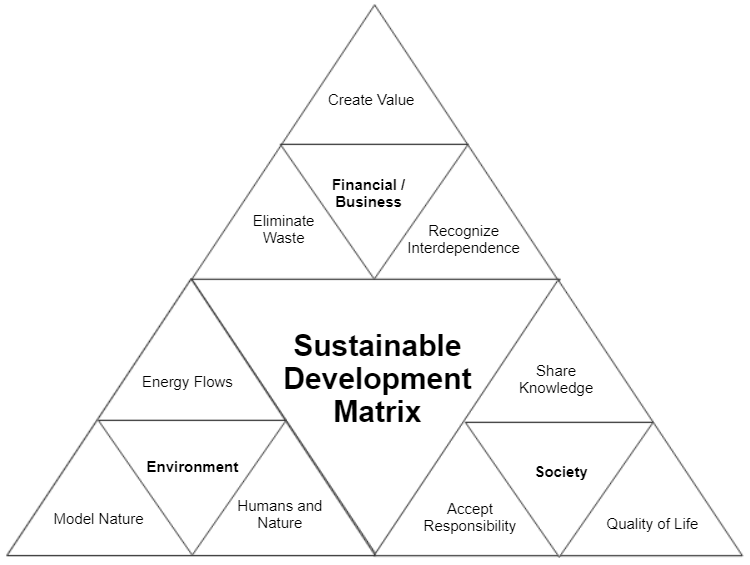
Generally, the concept of sustainability involves the use of available resources to cater for the needs of current generations while ensuring that the same resources would be available to meet the needs of future generations. In its broad context, sustainability has three pillars, namely: financial or business, social and environment. Using the sustainable development matrix as a guide, the financial pillar has to do with responsible business by corporations and their relations with stakeholders while the social pillar tackles the creation of value for society. The environmental pillar concerns itself with responsibly managing natural resources in a way that is beneficial to everyone.
One issue that has continuously been of keen interest to world leaders, business leaders and captains of industry is climate change. Climate change involves the rampant and continuous transformation of the world’s climate pattern leading to harsh conditions as a result of increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Interestingly, emissions of greenhouse gases are largely caused by human activities.
Data from Oxford University shows that emissions of carbon dioxide has grown over time due to several reasons with the most dominant been the rise of industrial revolution. For instance, based on OECD data, in 2020 Asia Pacific, North America, Europe, Middle East and Africa emitted 16.75 billion metric tons, 5.3 billion metric tons, 3.59 billion metric tons, 2 billion metric tons and 1.19 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide respectively. Emissions from aforementioned continents were relatively lower decades ago. Although the industrial revolution benefited humanity, it also witnessed an upsurge in usage of unsustainable energy sources such as coal and fossil fuel in which petrol and diesel were widely used to produce energy for manufacturing plants, heating, lightening, etc. This phenomenon resulted in the gradual rise of global temperature leading to changes in weather patterns bringing out negative effects such as wild fire and hurricanes, droughts and heat waves, and rise of sea levels.
In 2015, world leaders took action by signing an international treaty now known as Paris Agreement to guide countries on mitigation, adaptation and financing measures required to combat climate change. Following from this, efforts were made globally to curb climate change through building of sustainable ecosystems and decreasing carbon footprint of industries. This resulted in new strategies with terminologies such as net zero, energy transition and decarbonisation dominating discourses.
The realignment of supply chains as a result of achieving net zero has affected almost all industries including the transportation sector which is one of the key sectors that contributes high carbon dioxide emissions globally leading to disruptive innovation in the transportation sector. The transportation sector has therefore been bombarded with new innovations that are intended to make the world a better place for both current and future generations through the development and subsequent manufacturing of alternative vehicles that emits less carbon dioxide such as electric vehicles.

The continuous increase in demand for products globally as a result of population growth, globalisation, etc., has made green supply chain management more prominent these days. It is now significant to ensure that designing, sourcing and choosing materials, producing and distributing products and services to consumers and managing end of life usage of these products are done in a sustainable way. However integrating environmental philosophy into supply chain management might be a complex undertaken for most industries.
Using the automobile industry as a case study, adopting the circular economy which emphasises on recycling and reusing materials from finished products over a long period of time would ensure that resources are used efficiently thereby reducing waste and achieving higher sustainability ratings. However, automobiles have over 30,000 parts, which makes it extremely difficult to make the supply chain entirely sustainable.
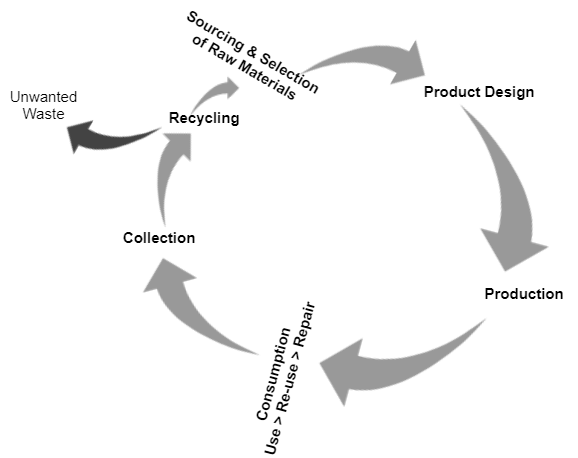
The introduction of alternative fuel vehicles of which electric vehicles are topical currently, unfortunately do not also solve the larger environmental issues. This is because sustainably disposing electric vehicle components such as batteries is a challenge. Beyond that, to achieve 100% supply chain sustainability, it must be ensured that input resources and transformation processes of an operation is undertaken sustainably, thus raw materials, product designs, production, end-user usage, and waste disposal must be deeply rooted in the concept of sustainability.
Irrespective of the hurdles, alternative fuel vehicles drastically helps to reduce tailpipe emissions which is vital in curbing climate change. Europe, North America and Asia have all made progress with alternative fuel vehicles in terms of market penetration and consumer adoption comparatively to Africa.
In a quest to decarbonize the world through reduction of carbon dioxide emissions in heavy emitting sectors such as the global transportation sector and achieve net zero, mass production of electric vehicles is significant because of the purchase price and monthly running cost which have been identified as factors that prevents adoption of electric vehicles in developing countries.
Africa is vital to reducing emissions in the transportation sector because of the continent’s demographics and socio-economic factors which is relevant in today’s world. This is because Africa is home to over one billion population out of which half is youthful. Africa’s middle class has increased steadily for the past three decades. With the introduction of a continental free trade agreement in Africa, it is expected that industries will grow leading to rise of the middle class population. This phenomenon is expected to result in increase in disposable income of the middle class and with road transportation been a major form of mobility in Africa especially for the middle class, conventional vehicles (powered with fossil fuel) sales are expected to increase in the future, thus up to 10 million cars per year by 2025. The rise of road vehicles in the world’s second most populous continent will present both threats and opportunities to the global quest to achieve net zero. Mass production of less tailpipe carbon dioxide emitting vehicles is therefore one of the utmost ways to ensure that as the African market and middle class grows, the transportation industry in Africa becomes environmentally sustainable thereby helping the world to curb climate change.

By: King A. Wellington (LinkedIn: King A. Wellington; Email: office@dbughana.com)
About the writer: King Adawu Wellington is a business strategist with expertise
in executing projects and helping companies achieve their goals in diverse industries.













